
How to Write an RFP: 2026 Guide
Complete RFP writing guide for 2026. Learn the 10 essential components, step-by-step process, and templates that get quality vendor responses.
SpecLens Team
Procurement & AI Experts
Why Writing a Great RFP Matters
A Request for Proposal (RFP) is one of the most critical documents in the procurement process. A well-crafted RFP attracts qualified vendors, ensures accurate proposals, and sets the foundation for successful partnerships. Yet, 62% of procurement professionals report that poorly written RFPs lead to misaligned proposals and procurement delays.
Whether you're procuring IT equipment, manufacturing machinery, construction materials, or professional services, your RFP determines the quality of responses you'll receive. This comprehensive guide will show you how to write an RFP that gets results. You may also want to use our vendor selection criteria checklist alongside this guide.
What is an RFP?
An RFP (Request for Proposal) is a formal business document that solicits proposals from vendors to provide specific products or services. Unlike a simple quote request, an RFP includes:
- Detailed project requirements and specifications
- Evaluation criteria for vendor selection
- Timeline and milestones for the project
- Budget parameters and payment terms
- Submission guidelines and deadlines
When Should You Use an RFP?
RFPs are ideal when:
- You need to compare multiple vendors on various criteria (not just price)
- The project is complex with specific technical requirements
- You want vendors to propose innovative solutions
- The purchase value exceeds your organization's threshold (typically $50,000+)
- You need formal documentation for compliance or approval processes
RFP vs RFQ vs RFI: Use an RFP when you need detailed proposals with solutions. Use an RFQ (Request for Quotation) when you know exactly what you want and only need pricing. Use an RFI (Request for Information) when you're still researching options.

The 10 Essential Components of an RFP
Every effective RFP includes these critical sections:
1. Executive Summary
Begin with a concise overview (1-2 pages) that includes:
- Company background: Who you are and what you do
- Project overview: What you're looking to procure
- Key objectives: What success looks like
- Timeline: When you need proposals and when the project starts
This section should be compelling enough to attract top vendors while filtering out those who aren't a good fit.
2. Company Information
Provide context about your organization:
- Company history and mission
- Industry and market position
- Current challenges or pain points
- Organizational structure (if relevant to the project)
- Key stakeholders and decision-makers
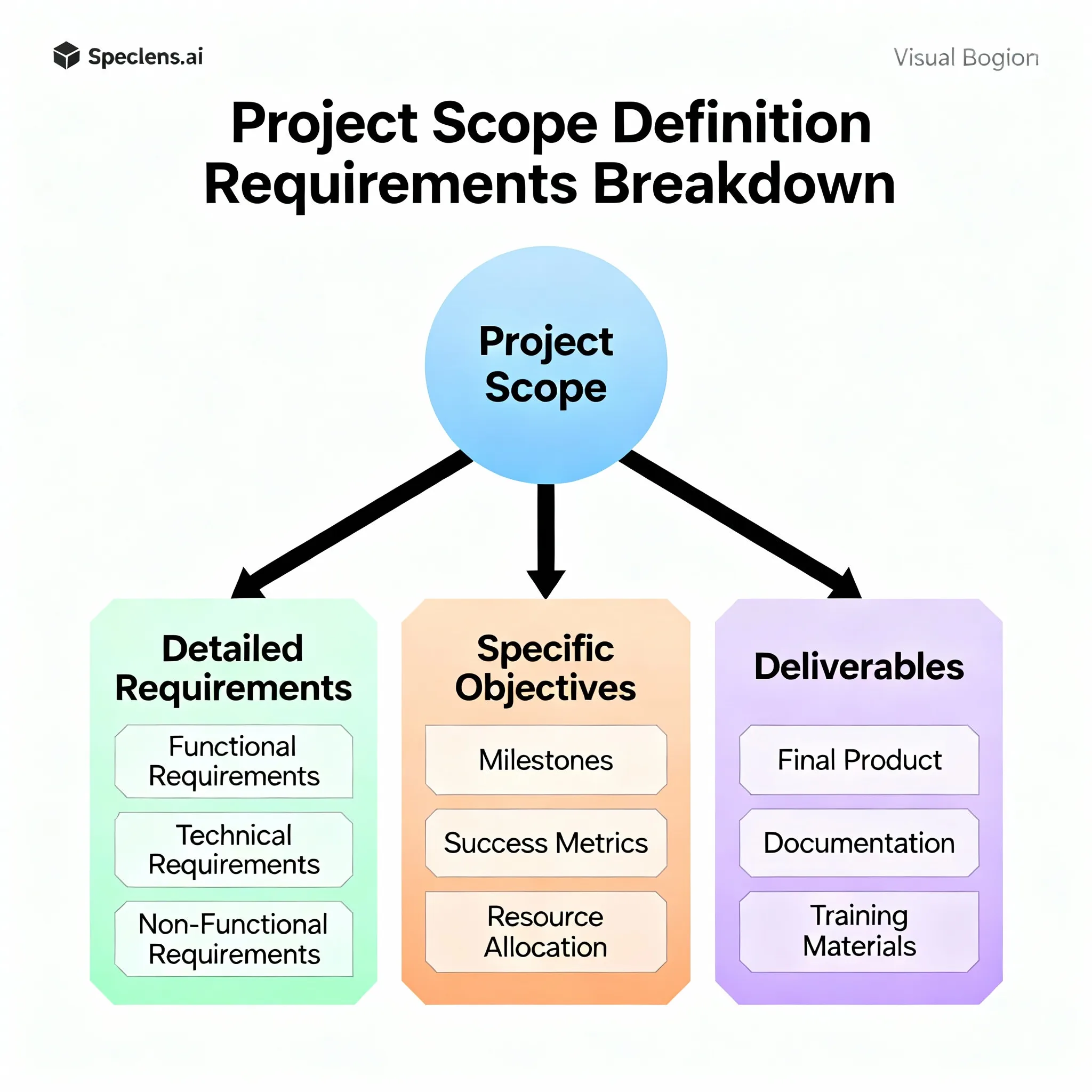
3. Project Scope and Objectives
This is the heart of your RFP. Be specific and comprehensive:
- Detailed requirements: List all functional and technical specifications
- Deliverables: Exactly what you expect to receive
- Success metrics: How you'll measure project success
- Constraints: Any limitations (budget, timeline, technical)
- Integration needs: How the solution must work with existing systems
Pro Tip: Use clear, specific language. Instead of "We need a high-performance server," write "We need a server with minimum 32GB RAM, 1TB SSD storage, and ability to handle 10,000 concurrent users."
4. Technical Specifications
Provide detailed technical requirements:
- Performance criteria: Speed, capacity, throughput requirements
- Compatibility requirements: Must integrate with existing systems
- Standards compliance: Industry certifications (ISO, CE, UL, etc.)
- Security requirements: Data protection and access controls
- Scalability needs: Future growth considerations
Organize specifications in a table format for easy reference and vendor response.
5. Timeline and Milestones
Create a clear project schedule:
- RFP release date: When the RFP is distributed
- Question deadline: Last day for vendor questions
- Proposal due date: Submission deadline
- Evaluation period: When you'll review proposals
- Vendor presentations: If applicable, when shortlisted vendors present
- Award notification: When the winning vendor is announced
- Project start date: When work begins
- Project milestones: Key deliverable dates
- Project completion: Final delivery date
Allow sufficient time for vendors to prepare quality proposals—typically 3-4 weeks minimum for complex projects.
6. Budget Information
Transparency about budget helps vendors propose realistic solutions:
- Budget range: Provide at least a general range if not an exact figure
- Pricing structure: Specify how you want pricing presented (itemized, bundled, etc.)
- Payment terms: Your payment schedule preferences
- Cost breakdown requirements: Request separate pricing for different components
Common Mistake: Hiding your budget often backfires. Vendors may propose solutions outside your range, wasting everyone's time. Being transparent attracts proposals that fit your constraints.
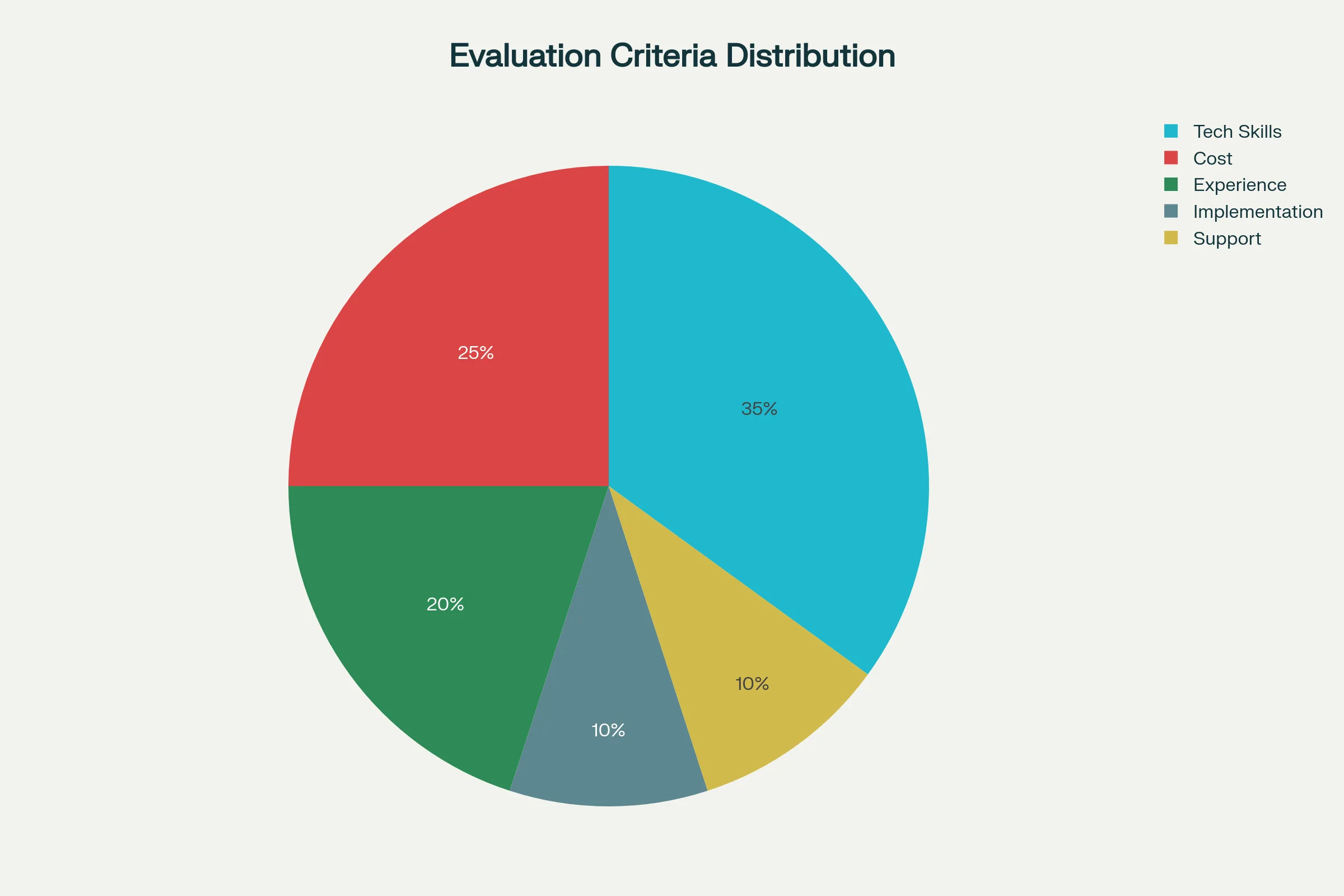
7. Evaluation Criteria
Tell vendors exactly how you'll evaluate proposals. Use weighted scoring:
- Technical capabilities (35%): Meeting specifications and requirements
- Cost (25%): Total cost of ownership, not just purchase price
- Experience and references (20%): Track record and client testimonials
- Implementation plan (10%): Methodology and timeline
- Support and maintenance (10%): Post-sale service and warranties
Adjust weights based on what matters most to your project. Being transparent about evaluation criteria helps vendors tailor their proposals. Consider using a structured vendor scorecard for ongoing evaluation.
8. Vendor Requirements
Specify what you need from vendors:
- Company information: Years in business, size, locations
- Financial stability: Proof of financial health (for large projects)
- Certifications: Required industry certifications or compliance
- References: Number and type of client references required
- Case studies: Examples of similar projects
- Team qualifications: Experience and expertise of assigned staff
- Insurance: Liability coverage requirements
9. Submission Guidelines
Make it easy for vendors to submit compliant proposals:
- Format requirements: Specify file formats (PDF, Word, Excel)
- Page limits: Prevent overly long proposals
- Required sections: List mandatory proposal components
- Submission method: Email, portal, physical delivery
- Number of copies: If physical copies are needed
- Contact information: Who to contact with questions
- Deadline: Date and time proposals are due
Pro Tip: Provide an RFP response template to ensure all vendors address the same questions in the same order. This makes comparison infinitely easier.
10. Terms and Conditions
Include legal and contractual information:
- Confidentiality: How proposal information will be handled
- Ownership: Who owns intellectual property created
- Contract terms: Standard terms and conditions
- Right to reject: Your right to reject any or all proposals
- Negotiation rights: Your right to negotiate with multiple vendors
- Compliance requirements: Legal and regulatory requirements
Have your legal team review this section to ensure it protects your organization's interests.
Step-by-Step RFP Writing Process
Follow this proven 8-step process to create an effective RFP:
Step 1: Assemble Your RFP Team
Gather stakeholders from relevant departments:
- Project sponsor: Executive who champions the project
- End users: People who will use the product/service
- Technical experts: Staff who understand specifications
- Procurement lead: Manages the RFP process
- Finance representative: Oversees budget and contracts
- Legal counsel: Reviews terms and conditions
Step 2: Define Requirements
Conduct workshops to identify and document:
- Current state: What you have now and its limitations
- Future state: What you want to achieve
- Must-have requirements vs. nice-to-have features
- Technical constraints and integration needs
- Budget range and timeline expectations
Create a requirements traceability matrix to ensure nothing is missed.
Step 3: Research the Market
Before writing your RFP:
- Research potential vendors and their capabilities
- Review similar procurement projects in your industry
- Understand current market pricing
- Identify industry best practices and standards
- Consider issuing an RFI first for complex projects
Step 4: Write the RFP Document
Use clear, professional language:
- Be specific: Avoid vague terms like "high quality" or "fast"
- Be consistent: Use the same terminology throughout
- Be realistic: Don't ask for impossible requirements
- Be organized: Use numbered sections and clear headings
- Be complete: Include all information vendors need
Writing Tip: Have someone unfamiliar with the project read your RFP. If they can't understand what you're asking for, vendors won't either.

Step 5: Review and Refine
Before releasing your RFP:
- Have all stakeholders review and approve
- Check for conflicting requirements
- Verify all specifications are accurate
- Ensure timeline is realistic
- Proofread for errors and typos
- Have legal review terms and conditions
Step 6: Distribute the RFP
Send your RFP to qualified vendors:
- Create a vendor list (aim for 5-10 qualified vendors)
- Use a secure distribution method
- Track who received the RFP
- Set up a system for vendor questions
- Consider posting publicly if required by policy
Step 7: Manage the Q&A Process
Handle vendor questions professionally:
- Designate a single point of contact
- Set a deadline for questions
- Share all questions and answers with all vendors (anonymously)
- Issue addendums if requirements need clarification
- Extend deadlines if major clarifications are needed
Transparent Q&A ensures all vendors have the same information and can compete fairly.
Step 8: Receive and Acknowledge Proposals
When proposals arrive:
- Log receipt time and date
- Confirm completeness
- Send acknowledgment to vendors
- Maintain confidentiality
- Store securely until evaluation begins
RFP Templates by Industry
Different industries require different RFP approaches. Here are considerations for common sectors:
IT & Technology RFPs
- Emphasize security requirements and certifications
- Detail integration needs with existing systems
- Include scalability and performance benchmarks
- Specify data backup and disaster recovery requirements
- Request information about software updates and support
Manufacturing Equipment RFPs
- Specify production capacity requirements
- Include quality control and inspection criteria
- Detail maintenance and spare parts availability
- Request information about training and documentation
- Include safety certifications and compliance
Construction & Building RFPs
- Detail architectural and engineering requirements
- Include material specifications and standards
- Specify permitting and compliance needs
- Request project management methodology
- Include safety protocols and insurance requirements
Healthcare Equipment RFPs
- Emphasize FDA approvals and medical certifications
- Detail clinical efficacy requirements
- Include patient safety specifications
- Request biocompatibility and sterilization information
- Specify warranty and service requirements

Common RFP Mistakes to Avoid
1. Being Too Vague
Problem: "We need a high-performance solution."
Solution: "We need a solution that processes 1,000 transactions per second with 99.99% uptime."
2. Unrealistic Timelines
Giving vendors only 1-2 weeks to respond to a complex RFP results in rushed, low-quality proposals. Allow 3-4 weeks minimum for comprehensive responses.
3. Asking for Too Much Information
While you want comprehensive proposals, requiring 100+ page responses discourages vendors and makes comparison difficult. Focus on what you truly need to make a decision.
4. Not Providing Budget Guidance
Hiding your budget leads to proposals ranging from $50,000 to $500,000. Provide at least a range so vendors can propose appropriate solutions.
5. Asking Leading Questions
Questions like "How does your solution exceed industry standards?" assume it does. Ask neutral questions like "How does your solution compare to industry standards?"
6. Ignoring Vendor Questions
If vendors are asking questions, your RFP isn't clear enough. Answer promptly and share responses with all vendors.
7. No Clear Evaluation Criteria
Without documented evaluation criteria, the process becomes subjective and may face challenges. Define and publish your scoring methodology upfront.
8. Copy-Pasting Old RFPs
Each project is unique. Using outdated RFP templates can include irrelevant requirements or miss new considerations.
Quality Check: Before sending your RFP, ask yourself: "Could I write a compliant proposal based on this document?" If not, revise for clarity.
How to Evaluate RFP Responses
Once proposals arrive, follow a structured evaluation process:
1. Initial Screening
- Verify proposals were submitted on time
- Check that all required sections are included
- Confirm vendors meet mandatory requirements
- Eliminate non-compliant proposals
2. Detailed Evaluation
- Create a scoring matrix based on your evaluation criteria
- Have multiple evaluators score independently
- Compare specifications side-by-side
- Calculate total cost of ownership, not just purchase price
- Verify vendor claims with references
3. Shortlist and Presentations
- Select top 2-4 vendors for detailed review
- Invite vendors to present their solutions
- Ask clarifying questions
- Request product demonstrations
- Visit vendor facilities or reference sites if possible
4. Final Selection
- Consolidate all evaluation scores
- Consider both quantitative and qualitative factors
- Negotiate with top vendor(s)
- Get stakeholder approval
- Award the contract
Pro Tip: Use AI-powered comparison tools like SpecLens to extract specifications from vendor proposals and create side-by-side comparison matrices automatically. This saves days of manual work and reduces errors in the evaluation process.
RFP Best Practices from Procurement Experts
1. Start with a Pre-RFP Market Analysis
Before writing your RFP, conduct informal vendor discussions or issue an RFI. This helps you understand what's possible, what's standard, and what vendors can realistically deliver.
2. Use a Standardized Template
Create an organizational RFP template that includes all standard sections. This ensures consistency and reduces time writing future RFPs.
3. Include a Response Template
Provide vendors with a structured response template. When all vendors answer the same questions in the same format, comparison becomes dramatically easier.
4. Be Transparent About Evaluation
Publish your evaluation criteria and scoring weights. Transparency leads to better proposals tailored to your actual needs.
5. Set Realistic Timelines
Allow adequate time for vendors to develop quality proposals. Complex projects may need 4-6 weeks. Also allow yourself enough time to evaluate properly.
6. Communicate Regularly
Keep vendors informed throughout the process. Let them know when evaluations are complete, when presentations will occur, and when decisions will be made.
7. Document Everything
Maintain records of all communications, questions, answers, and evaluation scores. This documentation is critical if your decision is ever questioned.
8. Learn and Improve
After each RFP process, conduct a retrospective. What worked? What caused confusion? Update your template based on lessons learned.
Free RFP Template
To help you get started, here's a basic RFP outline you can customize:
RFP Template Structure
1. Cover Page
- • RFP Title
- • Your Company Name
- • RFP Number/Reference
- • Issue Date
- • Submission Deadline
2. Table of Contents
• Numbered sections with page numbers
3. Executive Summary (1-2 pages)
- • Company overview
- • Project overview
- • Key objectives
- • Timeline summary
4. Company Background (2-3 pages)
- • Your organization's history
- • Industry and market position
- • Current situation and challenges
5. Project Scope & Requirements (5-10 pages)
- • Detailed functional requirements
- • Technical specifications
- • Performance criteria
- • Integration requirements
- • Deliverables
6. Timeline & Milestones (1-2 pages)
- • RFP schedule
- • Project schedule
- • Key milestones
7. Budget Information (1 page)
- • Budget range
- • Pricing format requirements
- • Payment terms
8. Evaluation Criteria (1-2 pages)
- • Scoring methodology
- • Weighted criteria
- • Selection process
9. Vendor Requirements (2-3 pages)
- • Company information required
- • Experience and qualifications
- • References
- • Certifications
10. Submission Guidelines (2 pages)
- • Format requirements
- • Submission method
- • Deadline
- • Contact information
11. Terms & Conditions (2-4 pages)
- • Legal terms
- • Confidentiality
- • Contract terms
- • Compliance requirements
12. Appendices
- • Response template
- • Technical diagrams
- • Supporting documents
How Technology Streamlines RFP Management
Modern procurement teams are using technology to improve both RFP creation and evaluation:
RFP Creation Tools
- Template libraries: Store and reuse standardized RFP sections
- Collaboration platforms: Allow stakeholders to contribute and review
- Requirement management: Track and trace all specifications
RFP Distribution Platforms
- Vendor portals: Centralized submission and Q&A
- Automated notifications: Keep vendors informed of deadlines
- Document tracking: Know who downloaded your RFP
Proposal Evaluation Tools
- AI specification extraction: Automatically extract specs from vendor documents
- Comparison matrices: Side-by-side spec comparison
- Scoring automation: Streamline evaluation process
- Collaboration features: Multiple evaluators can score simultaneously
SpecLens specializes in the evaluation phase, using AI to extract specifications from vendor proposals in any format (PDF, Word, Excel) and creating comprehensive comparison matrices automatically. This transforms the most time-consuming part of the RFP process from days of manual work to minutes of automated analysis.
Measuring RFP Success
Track these metrics to improve your RFP process:
- Response rate: Percentage of invited vendors who submitted proposals
- Proposal quality: How well proposals addressed requirements
- Time to award: Days from RFP release to contract award
- Number of clarifications: Fewer questions indicates a clearer RFP
- Stakeholder satisfaction: Did the process meet internal expectations?
- Post-implementation success: Did the selected vendor deliver as proposed?
Aim for 60-80% response rate from qualified vendors and complete the process in 60-90 days for standard projects.
Conclusion
Analyze Your RFP Complexity for Free
Estimate how long your RFP will take to review manually vs. with AI. Get recommendations on how to streamline your procurement process.
Analyze RFP Complexity →Writing an effective RFP is both an art and a science. It requires clear communication, thorough planning, and structured processes. A well-written RFP:
- Attracts qualified vendors who can meet your needs
- Results in comparable, high-quality proposals
- Makes evaluation faster and more objective
- Sets clear expectations for vendor relationships
- Provides documentation for compliance and approval
Follow the structure and best practices in this guide to create RFPs that get results. Remember to:
- Be specific about requirements and specifications
- Be transparent about budget and evaluation criteria
- Be realistic with timelines and expectations
- Be organized with clear structure and formatting
- Be responsive to vendor questions
The time invested in writing a great RFP pays dividends throughout the procurement process. Better proposals mean better decisions, better vendor relationships, and better outcomes for your organization.
Ready to streamline your RFP evaluation process? SpecLens uses AI to extract specifications from vendor proposals and create instant comparison matrices. What used to take days of manual work now takes minutes. Start your free trial and transform how you evaluate RFP responses.
Tags:
Related Articles
Compare Product Specifications (2026)
Master product specification comparison with proven strategies for vendor proposals and technical documents. Step-by-step guide for procurement teams.
Free TCO Calculator + Complete Guide (2026)
Use our free TCO calculator to compare vendor costs. Includes the TCO formula, hidden cost checklist, and real industry examples.
Vendor Negotiation: 6 Strategies for 2026
Negotiate better deals with suppliers using these 6 proven strategies. Save costs, secure better terms, and build stronger vendor relationships.
5 Procurement Best Practices for 2026
Stay ahead of the curve with these essential procurement best practices. From digital transformation to sustainability, learn how to modernize your sourcing.